Evolving Trends in Aluminum Panel Curtain Wall Applications
Aluminum panel curtain walls have become a prominent feature in modern architecture, offering both functional and aesthetic benefits. As design preferences and technological capabilities advance, new trends are shaping how these systems are specified and implemented. This article explores current developments in aluminum curtain wall applications, focusing on material innovations, design flexibility, performance enhancements, and installation efficiencies.
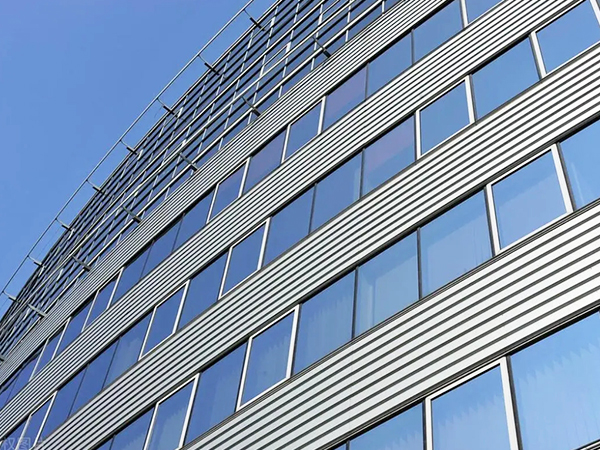

Material and Coating Advancements
Recent developments in aluminum alloys and surface treatments have expanded the possibilities for curtain wall performance. High-strength aluminum composites now allow for larger panel sizes with reduced supporting structures, enabling cleaner sightlines and more expansive glazing areas. Advanced coating technologies provide improved resistance to weathering while maintaining consistent color retention over extended periods.
Anodized and PVDF finishes continue to be widely used, with refinements in application techniques ensuring more uniform textures and color matching. New pretreatment processes enhance adhesion and durability, contributing to longer service life in various climatic conditions.
Design Flexibility and Customization
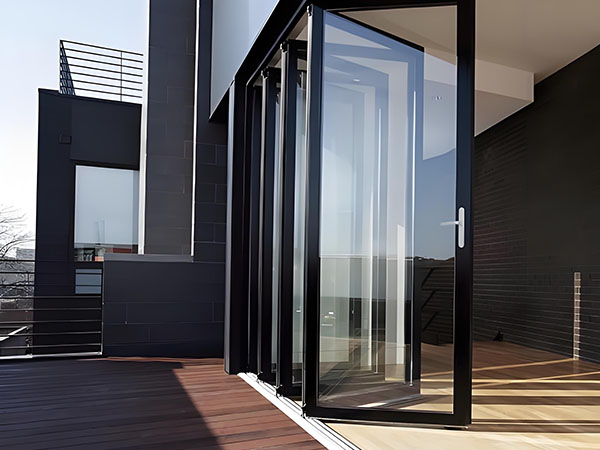
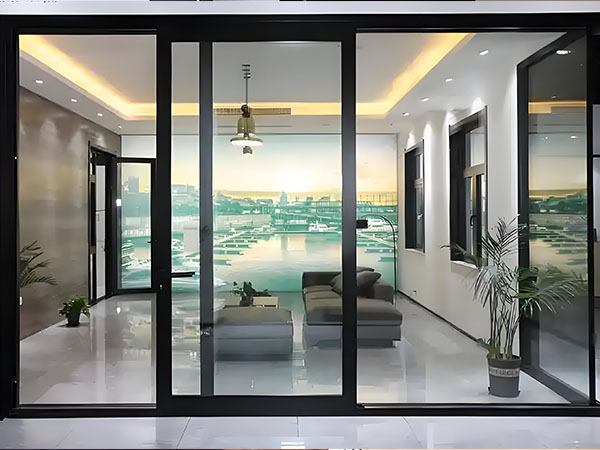
Architects are increasingly leveraging aluminum curtain walls to achieve distinctive building facades. The ability to fabricate panels in complex geometries—including curved, folded, and perforated designs—has grown with advancements in CNC machining and forming techniques. Custom panel shapes and sizes are now more feasible, allowing for unique architectural expressions.
Integrated shadow boxes, recessed joints, and varying depths create dynamic visual effects, while modular systems enable efficient replication of intricate patterns across large surfaces. The trend toward seamless, flush-mounted installations continues, minimizing visible fasteners for a sleek appearance.
Performance and Functional Improvements
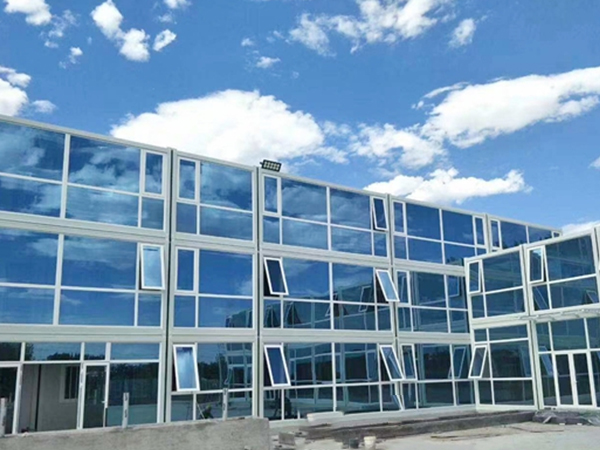
Modern aluminum curtain wall systems incorporate enhanced thermal and acoustic performance. Improved thermal breaks and insulating materials help meet stricter energy codes without compromising structural integrity. Multi-chambered framing profiles and optimized gasket systems contribute to better air and water infiltration resistance.
Structural silicone glazing techniques have evolved, allowing for greater glass spans and reduced aluminum framing visibility. Hybrid systems combining aluminum with other materials, such as stainless steel or reinforced polymers, provide additional strength where needed while maintaining design cohesion.
Installation and Fabrication Efficiency
Prefabrication and modular installation methods are gaining traction, reducing on-site labor and project timelines. Factory-assembled units, including pre-glazed panels, ensure higher quality control and minimize weather-related delays during construction. Digital modeling and BIM integration facilitate precise coordination between curtain wall systems and other building components.
Lightweight aluminum components simplify handling and transportation, while standardized connection systems streamline installation processes. These efficiencies contribute to cost predictability and reduced waste during construction.
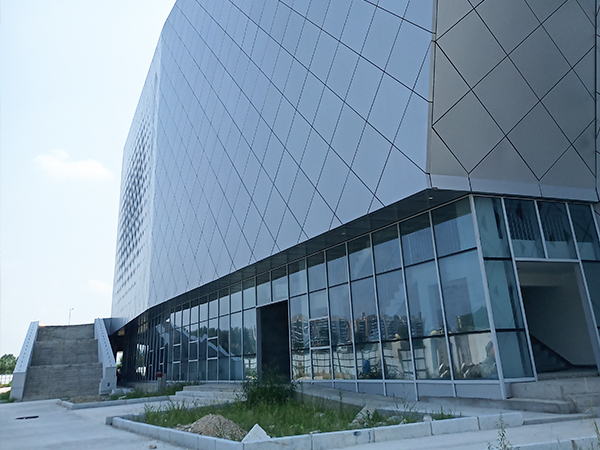

Conclusion
The application of aluminum panel curtain walls continues to evolve, driven by material advancements, design innovation, and improved performance characteristics. As fabrication and installation methods become more refined, these systems offer architects and developers greater flexibility in achieving both aesthetic and functional objectives. The ongoing development of aluminum curtain wall technology ensures its continued relevance in contemporary building design.